
Model Structure Overview
Rainfall-Runoff-Inundation (RRI) model is a two-dimensional model capable of simulating rainfall-runoff and flood inundation simultaneously (Sayama et al., 2012). The model deals with slopes and river channels separately. At a grid cell in which a river channel is located, the model assumes that both slope and river are positioned within the same grid cell. The channel is discretized as a single line along its centerline of the overlying slope grid cell. The flow on the slope grid cells is calculated with the 2D diffusive wave model, while the channel flow is calculated with the 1D diffusive wave model. For better representations of rainfall-runoff-inundation processes, the RRI model simulates also lateral subsurface flow, vertical infiltration flow and surface flow. The lateral subsurface flow, which is typically more important in mountainous regions, is treated in terms of the discharge-hydraulic gradient relationship, which takes into account both saturated subsurface and surface flows. On the other hand, the vertical infiltration flow is estimated by using the Green-Ampt model. The flow interaction between the river channel and slope is estimated based on different overflowing formulae, depending on water-level and levee-height conditions.
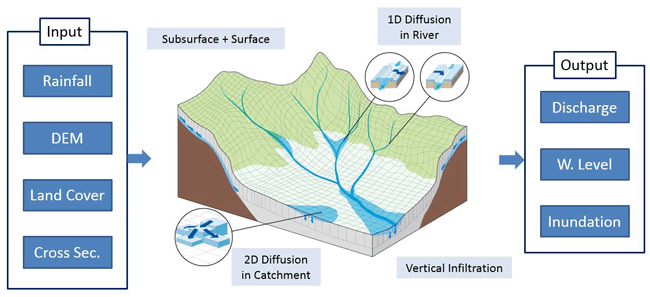 Schematic diagram of Rainfall-Runoff-Inundation (RRI) Model
Schematic diagram of Rainfall-Runoff-Inundation (RRI) Model Model Features
|

(Japanese)
