Proposed Manual of Repair Measures for Concrete Structures (Draft)
Figure 1. Structure of the Manual
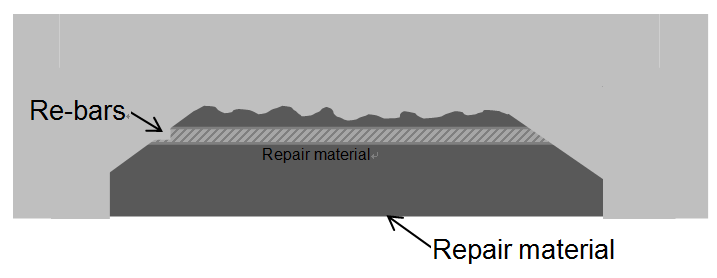
Figure 2. Image of Patching for
Concrete Structures

Figure 3. Example of Faulty Case
of Coating
Introduction
Concrete structures are used as various infrastructures, for instance bridges, tunnels, dams, and floodgates. Concrete structures that have been designed and executed using appropriate materials generally provide superior durability, and it used to be assumed that they did not have to be maintained after they were built.
However, some concrete structures were repaired after they are constructed. Reasons for this include their exposure to harsh environments not envisioned at the time they were designed, or the effects of deterioration mechanisms that were not fully understood at the time. Regarding the maintenance technique for concrete structures, from 1985 to 1987, under a general technology development project of the Ministry of Construction titled, "Development of a Technology for Improving the Durability of Concrete Structures (hereafter, "Durability Project")", an intensive study was carried out to draw up repair measures for deteriorated structures.
In order to repair a structure, it is necessary to consider the degree of deterioration of the structure to be repaired, the used materials, the deterioration environment and various other factors, which requires more advanced technological capabilities than when building new structures. Therefore, even after the Durability Project, further studies were undertaken in order to clarify precautions required when making repairs, using information not available when the study for the Durability Project was conducted.
The outcomes of research conducted in recent years have been compiled in the Manual of Repair Measures for Concrete Structures proposed by PWRI.
Outline of Research Outcomes
The Manual consists of Common Provisions, which summarize the procedure for selecting repair methods, and Provisions by Work Method, which summarizes precautions to be followed when using particular repair methods, and a collection of Faulty Repair Cases (Figure 1).
TWhen designing repairs to a concrete structure, it is necessary to select an appropriate repair method according to the state of the structure considering the mechanisms and degree of its deterioration. It is also essential to test repair materials to be used to confirm that they have the required properties. This manual includes methods for confirming the quality of materials used to perform the patching (work method that remove deteriorated concrete and replaces it with repair material: Fig. 2) for example.
TThere have also been cases where, even though the materials and work method selection were suitable, quantity control during execution was inadequate; resulting in the need for further repairs (Fig. 3). Based on these cases, the manual presents points that must be checked during execution of, for example, coating for concrete.
How to obtain the manual
For a free copy of the Manual of Repair Measures for Concrete Structures (Draft), visit the website of the Innovative Materials and Resources Research Center (iMaRRC) of the Public Works Research Institute (PWRI).
(Contact: Innovative Materials and Resources Research Center)
Development of a Wave Overtopping Prevention Fence by Using Folded Transparent Polycarbonate Sheets:Measures against Overtopping Waves on Coastal Roads
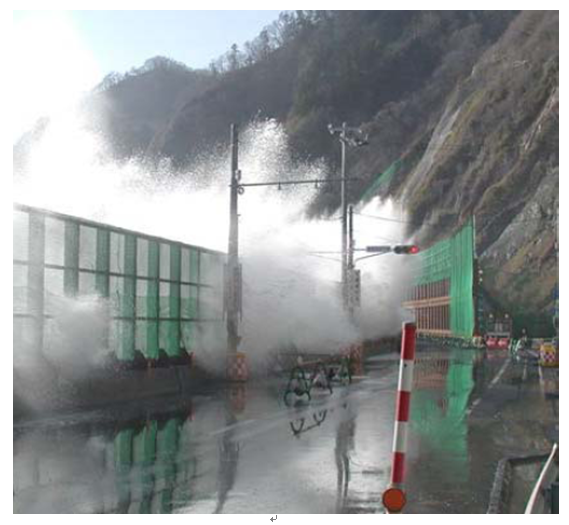

Figure 1 Wave overtopping
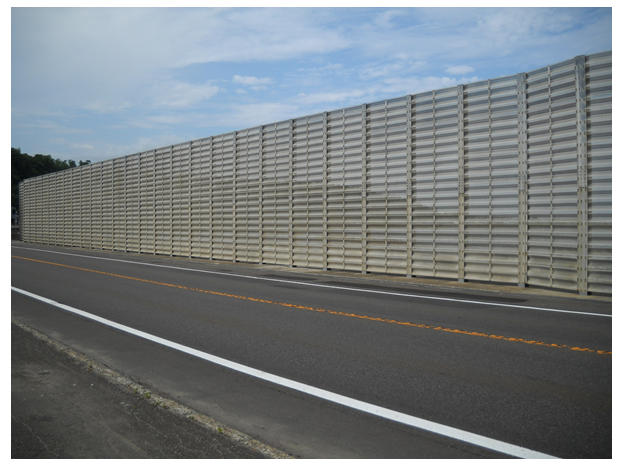

Figure 2 Conventional wave overtopping
prevention fences
(built using perforated steel sheets)
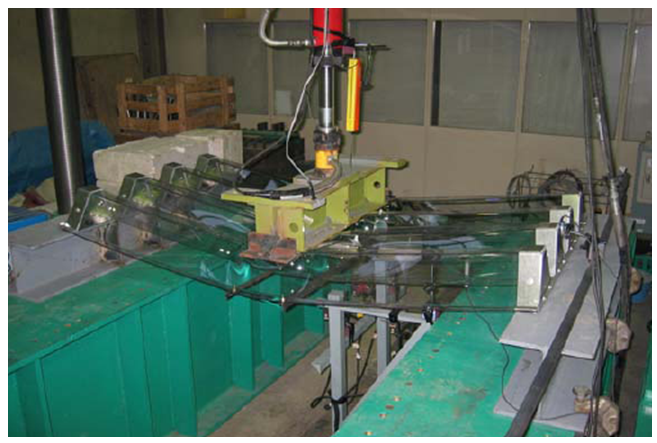

Figure 3 Loading test of folded
transparent PC sheets
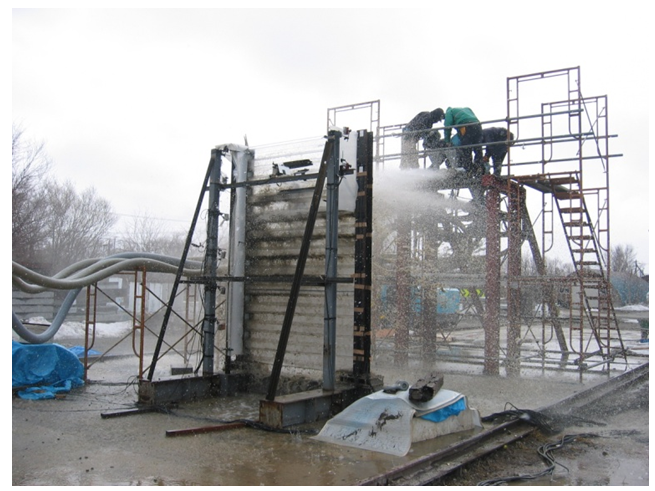

Figure 4 Wave overtopping simulation
(using water and gravel)
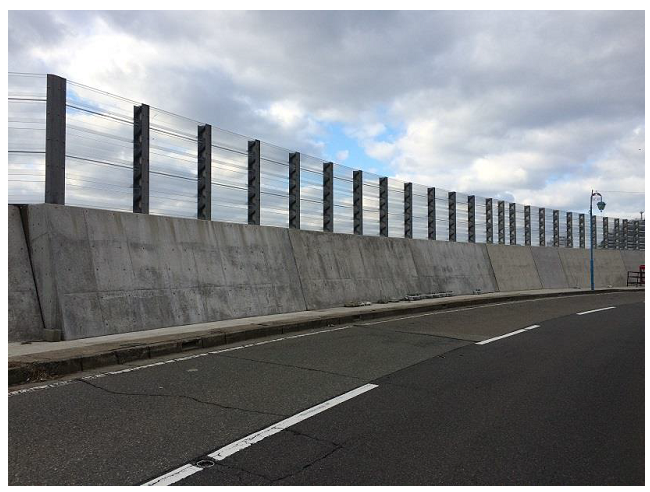

Figure 5 Fences that were installed
in Fukui Prefecture in 2014
1 Background to the research and development of the fence
Wave overtopping takes place under certain weather conditions along coastal roads (Figure 1) and can adversely affect the safety of road users. Additionally, traffic controls enforced due to wave-overtopping interfere with the daily lives and activities of local residents. Conventional fences built to protect road users from wave overtopping are made of perforated steel sheets (Figure 2).
These fences need to be resistant to huge wave pressure and fly rock. In recent years, these fences are increasingly required to allow the passage of light and to be built on the basis of aesthetic considerations. For this reason, the Structures Research Team of the Civil Engineering Research Institute for Cold Region developed a wave overtopping prevention fence that incorporates impact-resistant folded transparent polycarbonate sheets.
2 Fences built by using folded transparent PC sheets
The part of the fence that is directly exposed to waves is made of polycarbonate (PC) . The PC sheets used for the fences are transparent, resistant to impact, and weatherproof on both surfaces. Folded PC sheets are thinner and more resistant to impact than flat PC sheets. Folded PC sheets are supported by H-shaped steel posts secured to the foundation.
In the current research, the Structures Research Team has been conducting loading tests of full-size folded PC sheets in order to analyze the structural performance of these sheets and to examine methods of securing the sheets to posts (Figure 3). The test results show that folded PC sheets are strong enough to resist the design load. Wave overtopping simulations conducted by using a fence secured to a post confirmed that the fence had no problems in terms of translucency or resistance to water pressure and fly rock (Figure 4). Based on the results of test construction of fences, techniques for connecting folded PC sheets with each other have been reviewed.
The installation of wave overtopping prevention fences developed by the Structures Research Team started on national highways in Hokkaido. Recently, these fences have also been installed in other parts of Japan (Figure 5).
(Contact: Structures Research Team, Civil Engineering Research Institute for Cold Region)
